1. Qt 串口通讯¶
Qt串行端口(Qt Serial Port)提供基本功能,包括配置、I/O操作、获取和设置RS-232引脚的控制信号。
本章主要讲解QSerialPort模块,参考Qt例程,写一个非常简陋的串口助手。
鲁班猫板卡的串口资源以及串口使用可以参考下:https://doc.embedfire.com/linux/rk356x/linux_base/zh/latest/linux_app/uart/uart.html
1.1. Qt Serial Port¶
串口模块中两个类 QSerialPortInfo 和 QSerialPort
QSerialPort 提供访问串行端口的功能,继承于QIODevice
QSerialPortInfo 提供有关现有串行端口的信息
QSerialPortInfo使用静态函数生成QSerialPortInfo对象的列表,列表中的每个QSerialPortInfo对象代表一个串行端口,可以查询该端口的名称,系统位置,描述和制造商。
QSerialPortInfo::availablePorts()获取的串口信息,可以被QSerialPort用来设置串口参数。 我们可以使用QSerialPort类提供的方法来设置串口的相关参数:
setBaudRate() 设置波特率
setDataBits() 设置数据位
setParity() 设置校验位
setStopBits() 设置停止位
setFlowControl() 设置流控制
设置串口参数后,可以使用open()方法以只读(r/o)、仅写(w/o)或可读可写(r/w)模式打开它。 成功打开后,串口可以使用read()、readLine()或者readAll()来读取数据,使用 write()来读写数据到串口设备,不使用串口时使用close()关闭串口。
注意:串口始终以独占访问方式打开(其他进程或线程不能访问已打开的串口)。
串口使用过程中,可以通过readyRead()信号, 一旦知道串口已准备好读取或写入,就可以使用read()或write()方法。另外,还可以调用readLine()和readAll()便捷方法。 如果不是一次读取所有数据,则在将新的传入数据附加到QSerialPort的内部读取缓冲区后,其余数据将可供以后使用。 您可以使用setReadBufferSize()限制读取缓冲区的大小。
还有些功能可用于实现阻塞串行端口:
waitForReadyRead()阻止调用,直到可以读取新数据为止。 waitForBytesWritten()阻止调用,直到将一个有效载荷数据写入串行端口为止。
如果waitForReadyRead()返回false,则表示串口连接已关闭或数据传输发生了错误。 如果在任何时间点发生错误,QSerialPort将发出errorOccurred()信号,还可以调用error()来查找上次发生的错误的类型。
更多的串口模块信息可以参考下官方文档:https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtserialport-module.html
1.2. 串口例程¶
测试例程根据Qt官方 Terminal Example 进行了简单修改。 测试例程串口通讯使用异步(非阻塞)方法,发送操作后,立即返回。
1.2.1. 串口例程编写¶
创建项目例程文件:
创建SerialPort工程,基于QWidget
界面设计,设计一个串口通信界面(MainWindow)和一个串口设置对话框(SettingsDialog)
创建一个Console类,基于QPlainTextEdit,用于显示串口数据和输入发送数据
串口程序编写 :
使用 QSerialPortInfo::availablePorts() 获取当前设备识别到的串口
新建一个串口实例 QSerialPort,设置它的端口号,波特率等参数
绑定 QSerialPort 的 readyRead() 信号,自动接受串口数据
使用 QSerialPort 的 open() 函数打开串口
调用 read() 或 write() 进行数据收发
使用 QSerialPort 的 close() 函数关闭串口。
1.2.2. 核心代码讲解¶
Qt串口模块为一个附加模块,使用串口相关的类时,需要在pro工程文件中添加 QT += serialport
工程中有四个用户类:Console,SettingsDialog,Settings,MainWindow:
Console负责控制台相关的业务,例如显示串口数据;
SettingsDialog是一个QDialog类,其目的是用于设置串口的参数;
Settings是用来保存当前串口的参数的类,SettingsDialog的一个成员类;
MainWindow则进行串口数据的读写,UI相关的业务。
程序启动第一步就是初始化MainWindow,MainWindow构造函数中,创建了上面的类和一个串口类(QSerialPort)的实例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | QSerialPort *m_serial = nullptr;
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
m_ui(new Ui::MainWindow),
m_status(new QLabel),
m_console(new Console),
m_settings(new SettingsDialog),
m_serial(new QSerialPort(this))
{
m_ui->setupUi(this);
m_console->setEnabled(false);
setCentralWidget(m_console);
m_ui->actionConnect->setEnabled(true);
m_ui->actionDisconnect->setEnabled(false);
m_ui->actionQuit->setEnabled(true);
m_ui->actionConfigure->setEnabled(true);
m_ui->statusBar->addWidget(m_status);
initActionsConnections();
//关联信号与槽
connect(m_serial, &QSerialPort::errorOccurred, this, &MainWindow::handleError);
//关联串口readyRead信号和读取数据槽函数
connect(m_serial, SIGNAL(readyRead()), this, SLOT(readData()));
//关联信号与槽,用于串口发送Console输入的数据
connect(m_console, &Console::getData, this, &MainWindow::writeData);
//定时器,用于定时发送测试数据
timer = new QTimer();
connect(timer, SIGNAL(timeout()), this, SLOT(handletimeout()));
}
|
创建SettingsDialog实例的时候,会在构造函数中调用这个fillPortsInfo()函数, 此函数通过QSerialPortInfo::availablePorts()静态函数获取当前可获得的串口设备信息,将相关的端口号、可设置的参数,在SettingsDialog窗口显示出来:
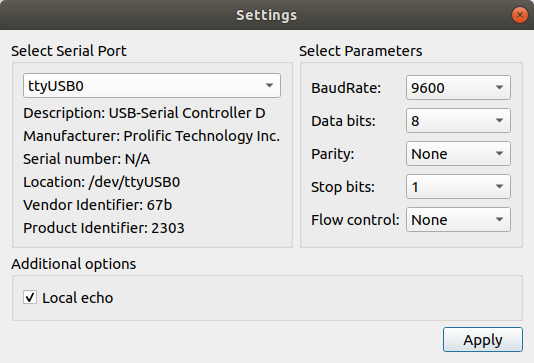
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | void SettingsDialog::fillPortsInfo()
{
m_ui->serialPortInfoListBox->clear();
QString description;
QString manufacturer;
QString serialNumber;
//获取获取设备串口信息
const auto infos = QSerialPortInfo::availablePorts();
for (const QSerialPortInfo &info : infos) {
QStringList list;
description = info.description();
manufacturer = info.manufacturer();
serialNumber = info.serialNumber();
list << info.portName()
<< (!description.isEmpty() ? description : blankString)
<< (!manufacturer.isEmpty() ? manufacturer : blankString)
<< (!serialNumber.isEmpty() ? serialNumber : blankString)
<< info.systemLocation()
<< (info.vendorIdentifier() ? QString::number(info.vendorIdentifier(), 16) : blankString)
<< (info.productIdentifier() ? QString::number(info.productIdentifier(), 16) : blankString);
m_ui->serialPortInfoListBox->addItem(list.first(), list);
}
m_ui->serialPortInfoListBox->addItem(tr("Custom"));
}
|
当点击设置串口的设置后,点击窗口的 Apply 时,就会自动调用updateSettings()来更新Settings中的串口信息。
在前面构造函数的initActionsConnections()中,会关联很多Action和操作,其中actionConnect操作时,会调用MainWindow::openSerialPort()函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | void MainWindow::openSerialPort()
{
//从SettingsDialog获取到Settings
const SettingsDialog::Settings p = m_settings->settings();
//根据Settings中的串口参数,配置串口,并读写方式打开串口
m_serial->setPortName(p.name); //串口名
m_serial->setBaudRate(p.baudRate); //波特率
m_serial->setDataBits(p.dataBits); //数据位
m_serial->setParity(p.parity); //校验位
m_serial->setStopBits(p.stopBits); //停止位
m_serial->setFlowControl(p.flowControl); //流控
if (m_serial->open(QIODevice::ReadWrite)) {
m_console->setEnabled(true);
m_console->setLocalEchoEnabled(p.localEchoEnabled); //回显
m_ui->actionConnect->setEnabled(false);
m_ui->actionDisconnect->setEnabled(true);
m_ui->actionConfigure->setEnabled(false);
showStatusMessage(tr("Connected to %1 : %2, %3, %4, %5, %6")
.arg(p.name).arg(p.stringBaudRate).arg(p.stringDataBits)
.arg(p.stringParity).arg(p.stringStopBits).arg(p.stringFlowControl));
//timer->start(1000);
} else {
QMessageBox::critical(this, tr("Error"), m_serial->errorString());
showStatusMessage(tr("Open error"));
}
}
|
在mainwindows构造函数中,之后会绑定串口的errorOccurred()和readyRead()信号, 当串口接收到数据的时候,就会触发readyRead()信号,随即调用readData()槽函数,使用readAll()去读取串口数据,并显示到控制台。 串口发生故障的时候,会触发errorOccurred(),程序通过handleError()显示错误,并关闭串口。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | connect(m_serial, &QSerialPort::errorOccurred, this, &MainWindow::handleError);
connect(m_serial, &QSerialPort::readyRead, this, &MainWindow::readData);
//connect(m_serial, SIGNAL(readyRead()), this, SLOT(readData()));
void MainWindow::readData()
{
const QByteArray data = m_serial->readAll();
m_console->putData(data);
}
void MainWindow::handleError(QSerialPort::SerialPortError error)
{
if (error == QSerialPort::ResourceError) {
QMessageBox::critical(this, tr("Critical Error"), m_serial->errorString());
closeSerialPort();
}
}
|
串口接收到数据时,就会自动触发readyRead()信号,控制台就会显示串口接受到的数据了。 关闭UI时,会调用MainWindow::closeSerialPort()关闭串口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | void MainWindow::closeSerialPort()
{
if (m_serial->isOpen())
m_serial->close();
showStatusMessage(tr("Disconnected"));
}
|
1.2.3. 编译构建¶
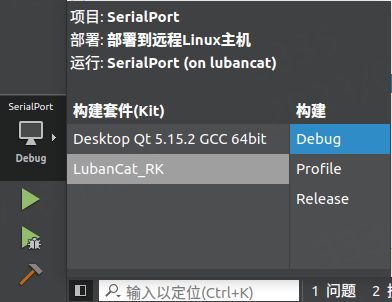
Ubuntu20.04主机上 选择 Desktop Qt 5.15.2 GCC 64bit 套件
LubanCat板卡上 选择 LubanCat-RK
注意 当两种构建套件进行切换时,请重新构建项目或清除之前项目。
1.2.4. 运行测试¶
编译构建后,复制可自行程序到LubanCat板卡上运行,需要将程序拷贝到LubanCat开发板中,可通过NFS或SCP命令, NFS环境搭建参考:https://doc.embedfire.com/linux/imx6/linux_base/zh/latest/linux_app/mount_nfs.html
SCP命令如下:
# 复制可执行程序到板卡(这里测试的是lubancat2板卡)
scp SerialPort cat@192.168.103.110:/home/cat/qt
教程测试使用lubancat2板卡,使用USB转串口线将lubancat2的串口3连接到PC。 同时开启下板卡的串口3,串口的开启参考下 《串口通讯教程》
在LubanCat上运行串口例程:
# 在debian10 带桌面的系统中运行,测试使用xcb
# 注意程序打开设备文件,需要root权限
sudo ./SerialPort -platform xcb
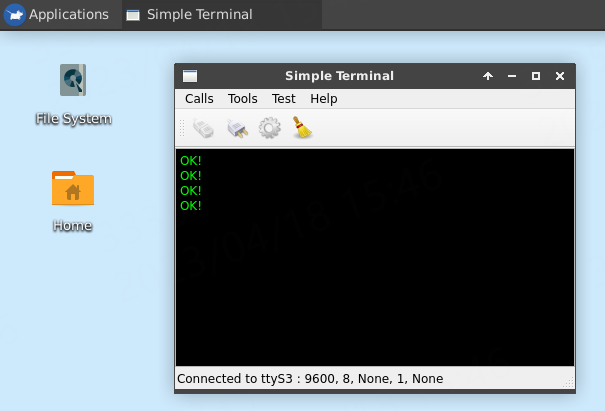
先点击界面的 tools-->config 可以对串口进行设置,点击串口的下拉框选择我们开启了的LubanCat2串口3(ttyS3):
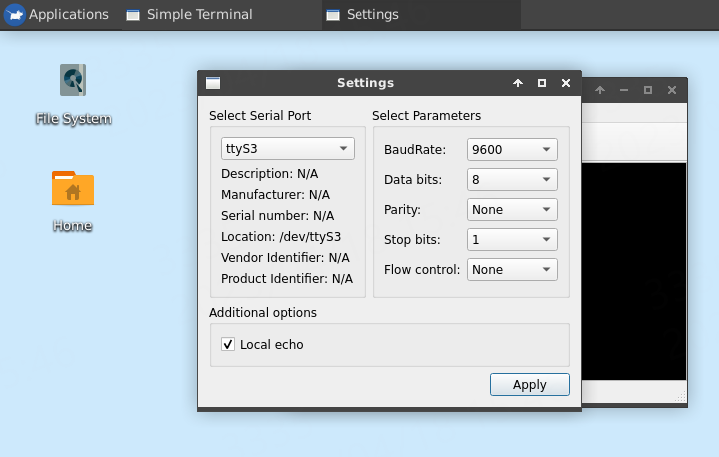
串口3的标识为ttyS3,我们设置波特率设置为9600。 然后点击连接,打开串口即可进行数据收发。
测试板卡数据发送,点击到Console上,输入需要发送的数据,然后回车,就会发送数据,
或者在窗口的工具栏有一个定时发送的测试功能,点击 Test -> start timer,运行在pc上的串口助手(需要设置一致的串口参数)就会定时收到 https://firebbs.cn:
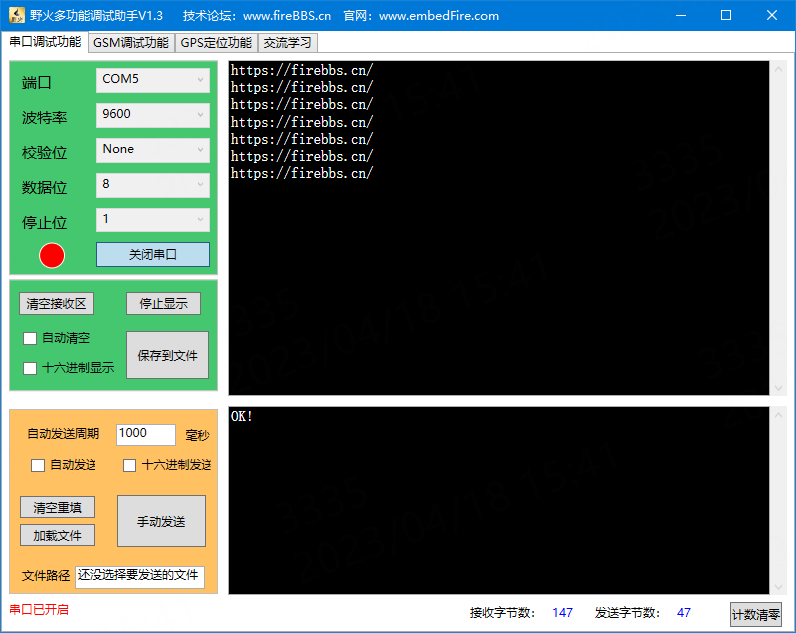
测试板卡数据接收测试,在PC串口助手上发送消息,在板卡上的串口工具就会显示: