14. 野火根文件系统定制¶
前一章节,介绍了如如何构建基础根文件系统,这一章节将讲解野火对基础根文件系统的定制。
在SDK编译流程及用户配置章节中,提供了一张SDK编译流程图,截取系统定制部分如下:
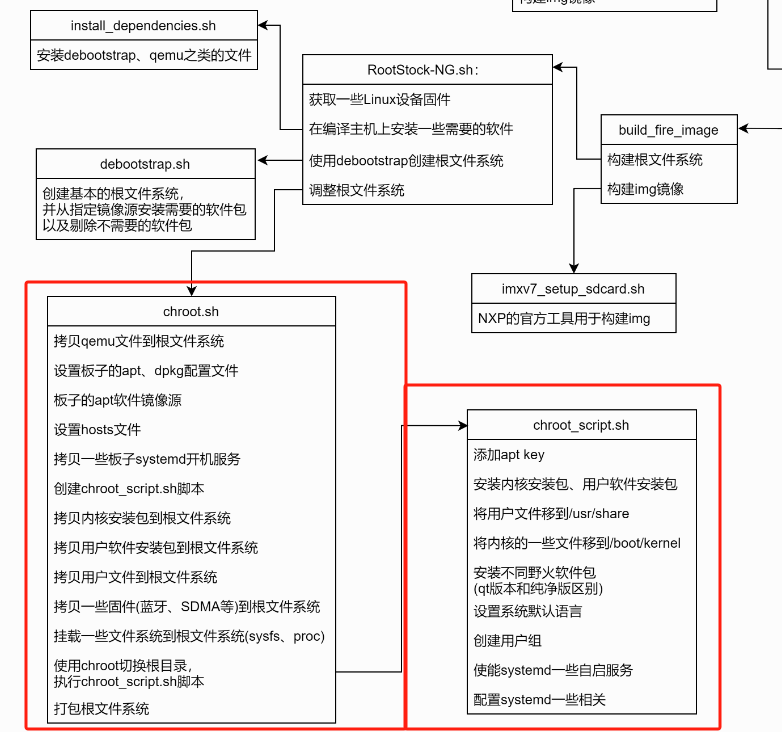
从上图可见,定制部分为chroot.sh脚本,具体路径为:ebf-image-builder/scripts/chroot.sh。由于脚本内容过长,下面将根据上图流程进行讲解。
14.1. chroot.sh脚本¶
14.1.1. 拷贝qemu文件到根文件系统¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | if [ "x${host_arch}" != "xarmv7l" ] && [ "x${host_arch}" != "xaarch64" ] ; then
if [ "x${deb_arch}" = "xarmel" ] || [ "x${deb_arch}" = "xarmhf" ] ; then
sudo cp $(which qemu-arm-static) "${tempdir}/usr/bin/"
fi
if [ "x${deb_arch}" = "xarm64" ] ; then
sudo cp $(which qemu-aarch64-static) "${tempdir}/usr/bin/"
fi
fi
|
以上内容是在检查主机架构${host_arch}和目标架构${deb_arch}的情况下,向临时目录${tempdir}复制不同架构对应的qemu静态二进制文件。
qemu-arm-static文件是用于在非ARM架构的系统上运行ARM架构的可执行文件。
14.1.2. 设置板卡的apt、dpkg配置文件¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | sudo mkdir -p "${tempdir}/etc/dpkg/dpkg.cfg.d/" || true
#generic apt.conf tweaks for flash/mmc devices to save on wasted space...
sudo mkdir -p "${tempdir}/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/" || true
#ubuntu apt verify
if [ "x${deb_distribution}" = "xubuntu" ] ; then
sudo touch "${tempdir}/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/99verify-peer.conf"
echo "Acquire { https::Verify-Peer false }" > "${tempdir}/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/99verify-peer.conf"
fi
....
if [ "x${deb_distribution}" = "xdebian" -o "x${deb_distribution}" = "lubancat" ] ; then
#apt: /var/lib/apt/lists/, store compressed only
case "${deb_codename}" in
jessie)
echo 'Acquire::GzipIndexes "true"; Acquire::CompressionTypes::Order:: "gz";' > /tmp/02compress-indexes
sudo mv /tmp/02compress-indexes "${tempdir}/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/02compress-indexes"
;;
stretch)
echo 'Acquire::GzipIndexes "true"; APT::Compressor::xz::Cost "40";' > /tmp/02compress-indexes
sudo mv /tmp/02compress-indexes "${tempdir}/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/02compress-indexes"
;;
buster|sid)
###FIXME: close to release switch to ^ xz, right now buster is slow on apt...
echo 'Acquire::GzipIndexes "true"; APT::Compressor::gzip::Cost "40";' > /tmp/02compress-indexes
sudo mv /tmp/02compress-indexes "${tempdir}/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/02compress-indexes"
;;
esac
|
在临时目录中创建一些定制的apt和dpkg配置文件,以适应特定的需求,比如节省空间或关闭HTTPS证书验证,根据不同的发行版本和是否存在代理信息,定制了 apt 的压缩方式和代理设置,以优化软件包管理器的性能和下载行为等。
14.1.3. 设置板卡的apt软件镜像源¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 | wfile="/tmp/sources.list"
echo "deb http://${deb_mirror} ${deb_codename} ${deb_components}" > ${wfile}
echo "#deb-src http://${deb_mirror} ${deb_codename} ${deb_components}" >> ${wfile}
echo "" >> ${wfile}
|
相关变量定义在ebf-image-builder/configs/common.conf,如果指定了DOWNLOAD_MIRROR == china,则默认使用北外的源。
14.1.4. 设置hosts文件¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | echo "127.0.0.1 localhost" > /tmp/hosts
echo "127.0.1.1 ${rfs_hostname}.localdomain ${rfs_hostname}" >> /tmp/hosts
echo "" >> /tmp/hosts
echo "# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts" >> /tmp/hosts
echo "::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback" >> /tmp/hosts
echo "ff02::1 ip6-allnodes" >> /tmp/hosts
echo "ff02::2 ip6-allrouters" >> /tmp/hosts
sudo mv /tmp/hosts "${tempdir}/etc/hosts"
sudo chown root:root "${tempdir}/etc/hosts"
sudo echo "Defaults lecture = never" > /tmp/privacy
sudo mv /tmp/privacy "${tempdir}/etc/sudoers.d/privacy"
echo "${rfs_hostname}" > /tmp/hostname
sudo mv /tmp/hostname "${tempdir}/etc/hostname"
sudo chown root:root "${tempdir}/etc/hostname"
|
修改主机的hosts文件,以确保正确的本地主机名解析和IPv6相关配置,修改系统的sudo配置,以禁止sudo在运行命令前显示任何的警告或提醒信息,并且修改主机的主机名为${rfs_hostname}。
rfs_hostname定义在ebf-image-builder/configs/user.conf,默认为lubancat。
14.1.5. 拷贝一些板卡systemd开机服务¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | ubuntu)
case "${deb_codename}" in
bionic|focal)
#while bb-customizations installes "generic-board-startup.service" other boards/configs could use this default.
sudo cp "${OIB_DIR}/target/init_scripts/systemd-generic-board-startup.service" "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/generic-board-startup.service"
sudo chown root:root "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/generic-board-startup.service"
sudo cp "${OIB_DIR}/target/init_scripts/bootlogo.service" "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/bootlogo.service"
sudo chown root:root "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/bootlogo.service"
sudo cp "${OIB_DIR}/target/init_scripts/actlogo.service" "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/actlogo.service"
sudo chown root:root "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/actlogo.service"
sudo cp "${OIB_DIR}/target/init_scripts/autowifi.service" "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/autowifi.service"
sudo chown root:root "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/actlogo.service"
distro="Ubuntu"
;;
esac
;;
esac
fi
if [ "x${deb_arch}" = "xarmel" ] ; then
sudo cp "${OIB_DIR}/target/init_scripts/systemd-generic-board-startup.service" "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/generic-board-startup.service"
sudo chown root:root "${tempdir}/lib/systemd/system/generic-board-startup.service"
distro="Debian"
fi
|
generic-board-startup初始化板卡服务,包括扩容、支持虚拟网卡、虚拟u盘、虚拟串口等功能。
bootlogo服务调用了/opt/scripts/boot/psplash.sh脚本,开机启动时的进度条程序就是由它调用执行的。
actlogo服务调用了/opt/scripts/boot/psplash_quit.sh脚本,野火的Qt app界面程序就是由它调用执行的。
autowifi服务WiFi自动链接服务。
14.1.6. 创建chroot_script.sh脚本¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | cat > "${DIR}/chroot_script.sh" <<-__EOF__
#!/bin/sh -e
export LC_ALL=C
export DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
...
__EOF__
|
脚本具体内容后面进行讲解,此处不展开。
14.1.7. 拷贝内核安装包到根文件系统¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 | if [ -d "${BUILD_DEBS}" ] ; then
sudo cp ${BUILD_DEBS}/${KERNEL_DEB} ${tempdir}/tmp
fi
|
拷贝内核deb包进系统,然后在chroot_script.sh中进行安装。
14.1.8. 拷贝用户软件安装包到根文件系统¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | if [ ! "x${repo_local_file}" = "x" ] ; then
...
if [ -d ${LOCAL_PKG} ] ; then
if [ -n "`find ${LOCAL_PKG} -maxdepth 1 -name '*.deb'`" ] ; then
mkdir ${tempdir}/tmp/local_pkg_deb
sudo cp ${LOCAL_PKG}/*.deb ${tempdir}/tmp/local_pkg_deb
fi
fi
fi
|
若用户想要添加一些自己编译的deb包,可将这些deb包放在ebf-image-builder/local_pkg目录下, 在构建镜像时将会自动安装。
14.1.9. 拷贝用户文件到根文件系统¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | if [ ! "x${repo_local_file}" = "x" ] ; then
if [ -d ${LOCAL_DIR} ] ; then
mkdir ${tempdir}/tmp/local_dir
sudo cp -r ${LOCAL_DIR}/* ${tempdir}/tmp/local_dir
fi
...
fi
|
用户若想要往板子里添加一些自己的文件,可将这些文件放在local_directory目录下, 在构建完整的镜像时,这些文件将被拷贝到/usr/share/目录下。
14.1.10. 拷贝一些固件到根文件系统¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | if [ "x${include_firmware}" = "xenable" ] ; then
if [ ! -d "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/" ] ; then
sudo mkdir -p "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/" || true
fi
if [ -d "${DIR}/git/linux-firmware/brcm/" ] ; then
sudo mkdir -p "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/brcm"
sudo cp "${DIR}/git/linux-firmware/LICENCE.broadcom_bcm43xx" "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/"
sudo cp "${DIR}"/git/linux-firmware/brcm/* "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/brcm"
fi
....
if [ -d "${DIR}/git/linux-firmware/rtl_nic/" ] ; then
sudo mkdir -p "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/rtl_nic"
sudo cp "${DIR}"/git/linux-firmware/rtl_nic/* "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/rtl_nic"
fi
if [ -d "${DIR}/git/linux-firmware/rtl_bt/" ] ; then
sudo mkdir -p "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/rtl_bt"
sudo cp "${DIR}"/git/linux-firmware/rtl_bt/* "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/rtl_bt"
fi
if [ -d "${DIR}/git/linux-firmware/imx/sdma" ] ; then
sudo mkdir -p "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/imx/sdma"
sudo cp "${DIR}"/git/linux-firmware/imx/sdma/* "${tempdir}/lib/firmware/imx/sdma"
fi
fi
|
固件下载地址定义在ebf-image-builder/scripts/RootStock-NG.sh,变量是git_clone_address=”https://gitee.com/Embedfire/linux-firmware.git”
14.1.11. 挂载一些文件系统到根文件系统¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | chroot_mount () {
if [ "$(mount | grep ${tempdir}/sys | awk '{print $3}')" != "${tempdir}/sys" ] ; then
sudo mount -t sysfs sysfs "${tempdir}/sys"
fi
if [ "$(mount | grep ${tempdir}/proc | awk '{print $3}')" != "${tempdir}/proc" ] ; then
sudo mount -t proc proc "${tempdir}/proc"
fi
if [ ! -d "${tempdir}/dev/pts" ] ; then
sudo mkdir -p ${tempdir}/dev/pts || true
fi
if [ "$(mount | grep ${tempdir}/dev/pts | awk '{print $3}')" != "${tempdir}/dev/pts" ] ; then
sudo mount -t devpts devpts "${tempdir}/dev/pts"
fi
}
|
作用是确保在指定的临时目录中正确地挂载了 sysfs、proc 和 devpts 文件系统,以便后续可以在该临时目录中创建 chroot 环境。
14.1.12. 使用chroot切换根文件目录¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 | sudo chroot "${tempdir}" /bin/bash -e chroot_script.sh
echo "Log: Complete: [sudo chroot ${tempdir} /bin/bash -e chroot_script.sh]"
|
作用是在指定的临时目录中创建一个 chroot 环境,并执行chroot_script.sh脚本,然后输出一条日志以记录这个操作的完成情况。
14.1.13. 打包根文件系统¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | value=$(du -sm "${DIR}/deploy/${export_filename}" | awk '{print $1}')
image_size=$(bc -l <<< "scale=0; ((($value * 1.2) / 1 + 0) / 4 + 1) * 4")
image_size=$(($image_size + $conf_boot_endmb + $conf_boot_startmb))
echo "Log: fiel_size:${value}M image_size:${image_size}M"
if [ -e /tmp/npipe ] ; then
rm /tmp/npipe
fi
mkfifo -m 777 /tmp/npipe
echo "$image_size" > /tmp/npipe &
|
主要完成了一些关于镜像大小计算、创建 tar 包、输出日志的操作。
14.2. chroot_script.sh脚本¶
注意chroot_script.sh脚本内容仍位于chroot.sh脚本中,以下仍然沿用chroot.sh脚本片段说法。
14.2.1. 添加apt key¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | install_pkg_updates () {
if [ -f /tmp/nodesource.gpg.key ] ; then
apt-key add /tmp/nodesource.gpg.key
rm -f /tmp/nodesource.gpg.key || true
fi
if [ -f /tmp/repos.azulsystems.com.pubkey.asc ] ; then
apt-key add /tmp/repos.azulsystems.com.pubkey.asc
rm -f /tmp/repos.azulsystems.com.pubkey.asc || true
fi
if [ "x${repo_rcnee}" = "xenable" ] ; then
apt-key add /tmp/repos.rcn-ee.net-archive-keyring.asc
rm -f /tmp/repos.rcn-ee.net-archive-keyring.asc || true
fi
if [ "x${repo_ros}" = "xenable" ] ; then
apt-key add /tmp/ros-archive-keyring.asc
rm -f /tmp/ros-archive-keyring.asc || true
fi
if [ "x${repo_external}" = "xenable" ] ; then
apt-key add /tmp/${repo_external_key}
rm -f /tmp/${repo_external_key} || true
fi
if [ "x${repo_flat}" = "xenable" ] ; then
apt-key add /tmp/${repo_flat_key}
rm -f /tmp/${repo_flat_key} || true
fi
|
主要目的是在系统中安装软件包更新所需的密钥,并在安装后清理临时文件。
14.2.2. 安装内核deb包和用户软件安装包¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | install_pkgs () {
if [ -f "/tmp/${KERNEL_DEB}" ] ; then
dpkg -i "/tmp/${KERNEL_DEB}"
rm -f /tmp/${KERNEL_DEB}
fi
if [ ! "x${repo_local_file}" = "x" ] ; then
...
if [ -d "/tmp/local_pkg_deb" ] ; then
dpkg -i /tmp/local_pkg_deb/*.deb
rm -rf /tmp/local_pkg_deb
fi
fi
|
主要是安装软件包,其中包括安装内核的 .deb 文件以及本地存储的软件包。在安装完成后,会对临时文件和目录进行清理。
14.2.3. 将用户文件移动¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | if [ ! "x${repo_local_file}" = "x" ] ; then
if [ -d "/tmp/local_dir" ] ; then
if [ ! -d "${system_directory}" ] ; then
mkdir -p ${system_directory}
fi
mv /tmp/local_dir/* ${system_directory}
rm -rf /tmp/local_dir
fi
|
作用是将本地存储的文件移动到系统目录/usr/share中,并在移动完成后清理临时目录。
14.2.4. 将内核文件移动¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | mkdir -p /boot/dtb_tmp
if [ -f /boot/dtbs/${LINUX}${LOCAL_VERSION}/${LINUX_MMC_DTB} ];then
cp /boot/dtbs/${LINUX}${LOCAL_VERSION}/${LINUX_MMC_DTB} /boot/dtb_tmp
cp /boot/dtb_tmp/${LINUX_MMC_DTB} /boot/dtbs/
fi
if [ -f /boot/dtbs/${LINUX}${LOCAL_VERSION}/${LINUX_NAND_DTB} ];then
cp /boot/dtbs/${LINUX}${LOCAL_VERSION}/${LINUX_NAND_DTB} /boot/dtb_tmp
#if [ -d "/boot/dtbs/${LINUX}${LOCAL_VERSION}/overlays" ] ; then
# mv /boot/dtbs/${LINUX}${LOCAL_VERSION}/overlays /boot
#fi
cp /boot/dtb_tmp/${LINUX_NAND_DTB} /boot/dtbs/
fi
rm /boot/dtbs/${LINUX}${LOCAL_VERSION} -rf
rm -rf /boot/dtb_tmp
mkdir -p /boot/kernel
mv /boot/*${LINUX}${LOCAL_VERSION}* /boot/kernelboot/kernel
|
作用是对设备树文件和内核文件进行管理,包括拷贝、删除和移动文件等操作。
14.2.5. 安装不同野火软件包¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 | if [ ! "x${repo_external_pkg_list}" = "x" ] ; then
echo "Log: (chroot) Installing (from external repo): ${repo_external_pkg_list}"
apt-get -y install ${repo_external_pkg_list} ${other_pk}
fi
|
repo_external_pkg_list定义在ebf-image-builder/configs/common.conf,主要区分qt版本、纯净版本以及桌面版本。
14.2.6. 设置系统默认语言¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | if [ "x\${pkg_is_not_installed}" = "x" ] ; then
if [ ! "x${rfs_default_locale}" = "x" ] ; then
case "\${distro}" in
Debian)
echo "Log: (chroot) Debian: setting up locales: [${rfs_default_locale}]"
sed -i -e 's:# ${rfs_default_locale} UTF-8:${rfs_default_locale} UTF-8:g' /etc/locale.gen
locale-gen
;;
Ubuntu)
echo "Log: (chroot) Ubuntu: setting up locales: [${rfs_default_locale}]"
locale-gen ${rfs_default_locale}
;;
esac
echo "LANG=${rfs_default_locale}" > /etc/default/locale
echo "Log: (chroot): [locale -a]"
locale -a
fi
else
dpkg_package_missing
fi
|
设置系统的区域和语言环境,包括生成区域和语言文件以及设置默认区域和语言环境。rfs_default_locale定义在ebf-image-builder/configs/user.conf。默认rfs_default_locale=”en_US.UTF-8”
14.2.7. 创建用户组¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | pass_crypt=\$(perl -e 'print crypt(\$ARGV[0], "rcn-ee-salt")' ${rfs_password})
useradd -G "\${default_groups}" -s /bin/bash -m -p \${pass_crypt} -c "${rfs_fullname}" ${rfs_username}
grep ${rfs_username} /etc/passwd
mkdir -p /home/${rfs_username}/bin
chown ${rfs_username}:${rfs_username} /home/${rfs_username}/bin
|
功能是创建一个新的用户,并设置其密码和家目录下的 bin 目录。用户和密码定义在ebf-image-builder/configs/user.conf。默认rfs_username=”debian”,rfs_password=”temppwd”。
14.2.8. 使能systemctl自启动服务¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | if [ -f /lib/systemd/system/generic-board-startup.service ] ; then
systemctl enable generic-board-startup.service || true
fi
if [ -f /lib/systemd/system/bootlogo.service ] ; then
systemctl enable bootlogo.service || true
fi
if [ -f /lib/systemd/system/haveged.service ] ; then
systemctl enable haveged.service || true
fi
if [ -f /lib/systemd/system/rng-tools.service ] ; then
systemctl enable rng-tools.service || true
fi
# if [ -f /lib/systemd/system/actlogo.service ] ; then
# systemctl enable actlogo.service || true
# fi
systemctl mask getty@tty1.service || true
systemctl enable getty@ttyGS0.service || true
systemctl mask wpa_supplicant.service || true
|
主要是针对特定 systemd 服务进行启用、屏蔽等操作,确保系统在启动时能按照需求正确配置和启动相关服务。
14.2.9. 配置systemctl相关¶
chroot.sh脚本片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | #kill systemd/connman-wait-online.service, as it delays serial console upto 2 minutes...
if [ -f /etc/systemd/system/network-online.target.wants/connman-wait-online.service ] ; then
systemctl disable connman-wait-online.service || true
fi
#We manually start dnsmasq, usb0/SoftAp0 are not available till late in boot...
if [ -f /lib/systemd/system/dnsmasq.service ] ; then
systemctl disable dnsmasq.service || true
fi
#We use, so make sure udhcpd is disabled at bootup...
if [ -f /lib/systemd/system/udhcpd.service ] ; then
systemctl disable udhcpd.service || true
fi
#Our kernels do not have ubuntu's ureadahead patches...
if [ -f /lib/systemd/system/ureadahead.service ] ; then
systemctl disable ureadahead.service || true
fi
#No guarantee we will have an active network connection...
#debian@beaglebone:~$ sudo systemd-analyze blame | grep apt-daily.service
# 9.445s apt-daily.services
if [ -f /lib/systemd/system/apt-daily.service ] ; then
systemctl disable apt-daily.service || true
systemctl disable apt-daily.timer || true
fi
....
|
主要是为了禁用一些与网络、系统优化、软件更新等相关的 systemd 服务,以确保系统在启动时不会受到这些服务的影响,并能更快地完成启动过程。
总的来说,定制系统基本涉及以下几个文件:
ebf-image-builder/scripts/chroot.sh
ebf-image-builder/configs/boards/ebf_imx_8m_mini.conf
ebf-image-builder/configs/user.conf
ebf-image-builder/configs/common.conf
相信结合前面的讲解,理解这几个文件的内容不是难事,具体没有讲解到的部分请读者自行研究。